
The electric light commercial vehicle (LCV) market in India is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing environmental awareness, government incentives, and advancements in electric vehicle (EV) technology. This report provides an in-depth analysis of the current market landscape, trends, competitive dynamics, and future outlook. Key findings indicate a significant rise in adoption rates, with major automakers and new entrants investing heavily in this segment. The market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 15% in the next five years. Recommendations include leveraging government incentives, focusing on technological advancements, and enhancing the EV charging infrastructure.

The purpose of this report is to analyse the electric LCV market in India, examining factors that influence its growth and the challenges it faces. The objective is to provide stakeholders with comprehensive insights to inform strategic decisions. This study covers market size, growth trends, competitive landscape, consumer preferences, and regulatory influences. The methodology includes a combination of primary research (surveys, interviews) and secondary research (industry reports, market databases).
The electric LCV market in India is defined as the segment of the automotive market that includes light commercial vehicles powered entirely by electric batteries. This market is growing due to a shift towards sustainable transportation solutions. In 2023, the market size was estimated at INR 2,500 crore, with projections indicating a potential market size of INR 5,000 crore by 2028. Key market trends include increased investment in EV technology, partnerships between automakers and technology firms, and rising consumer demand for eco-friendly vehicles.
The industry structure for electric LCVs in India comprises various key players including Tata Motors, Mahindra Electric, Ashok Leyland, and several start-ups like Euler Motors and Electric Vehicle Zone. The supply chain involves battery manufacturers, vehicle assemblers, and charging infrastructure providers. The competitive landscape is dynamic, with established players investing in R&D to enhance battery efficiency and new entrants innovating with cost-effective solutions. Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals a moderate threat of new entrants due to high capital requirements, significant bargaining power of suppliers, and intense competitive rivalry.
The target market for electric LCVs in India primarily includes small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) involved in logistics, e-commerce, and last-mile delivery services. These customers are driven by the need to reduce operational costs and comply with environmental regulations. Customer needs focus on cost-efficiency, reliability, and adequate range per charge. Demographically, the key buyers are typically located in urban and semi-urban areas, with a significant proportion of purchases made by businesses engaged in local deliveries. The electric LCV market in India can be segmented based on vehicle type, end-use industry, and geographic region. Each segment has unique characteristics and growth potential:
Current marketing strategies focus on highlighting the cost savings, environmental benefits, and operational efficiency of electric LCVs. Companies like Tata Motors and Mahindra Electric position their vehicles as both economical and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional LCVs. The marketing mix involves product strategies emphasizing advanced features like longer battery life, competitive pricing strategies including financing options, widespread availability through extensive dealer networks, and promotions leveraging digital platforms and green branding initiatives.

Electric LCVs in India are characterized by their zero-emission powertrains, reduced operational costs, and innovative features such as regenerative braking and telematics. Products like the Tata Ace EV and Mahindra eSupro offer competitive battery ranges and payload capacities. The product lifecycle for electric LCVs is in the growth phase, with continuous innovations enhancing battery life and reducing costs. R&D is focused on improving battery technology, increasing vehicle range, and reducing charging times to make electric LCVs more competitive with traditional vehicles.
The regulatory environment in India is increasingly favorable for electric LCVs, with government initiatives like the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme providing financial incentives and subsidies. Policies mandating stricter emission norms and promoting green transportation are driving adoption. Environmental factors include growing awareness of air pollution and climate change, pushing both consumers and businesses towards sustainable transport solutions. The regulatory framework supports the development of EV infrastructure, including charging stations and battery recycling programs.
The electric light commercial vehicle (LCV) market in India is influenced by several dynamic factors that drive its growth, present challenges, and offer opportunities for future expansion. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for stakeholders to navigate the market effectively.
1. Government Incentives and Policies:
2. Environmental Concerns:
3. Advancements in Battery Technology:
1. High Initial Costs:
2. Limited Charging Infrastructure:
3. Range Anxiety:
1. Expansion of Charging Infrastructure:
2. Technological Innovations:
3. Growing E-commerce and Logistics Sector:
1. Supply Chain Constraints:
2. Consumer Awareness and Perception:
3. Regulatory and Policy Uncertainty:
By analysing these market dynamics, stakeholders can develop strategies to leverage drivers and opportunities while addressing the restraints and challenges to foster the growth of the electric LCV market in India.
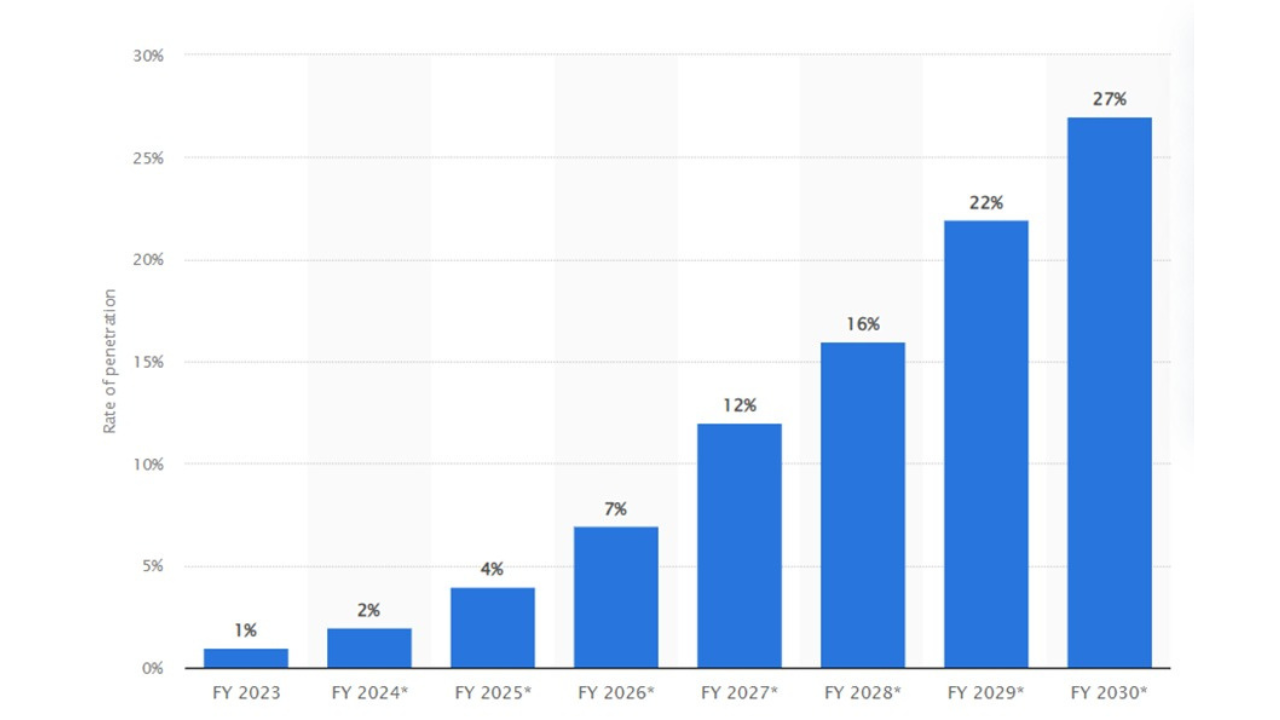
According to industry projections, the penetration of electric LCVs in the Indian market is expected to significantly increase over the next decade. By FY2030, it is anticipated that 20- 30% of all LCV sales will be electric, driven by a combination of regulatory support, technological advancements, and growing environmental consciousness among consumers and businesses. This shift is spearheaded by key players like Switch Mobility, which are investing in developing and deploying innovative electric mobility solutions. The company's initiatives highlight the broader market trend towards sustainability, with increasing investments in EV infrastructure and strategic partnerships aimed at accelerating the adoption of electric LCVs. This substantial growth projection underscores the market's potential and the critical need for continuous development in battery technology, cost reduction strategies, and robust charging networks.
Several Indian start-ups are making significant strides in the electric LCV market, contributing to its rapid growth and innovation. These start-ups are focusing on developing cost-effective, efficient, and sustainable electric mobility solutions tailored to the needs of the Indian market.

In conclusion, the electric LCV market in India is poised for substantial growth, supported by favourable regulatory policies, increasing environmental awareness, and technological advancements. The market's future outlook is optimistic, with significant opportunities for stakeholders across the value chain. Strategic recommendations include capitalizing on government incentives, investing in R&D to improve vehicle performance and affordability, and expanding the charging infrastructure to support widespread adoption.