
India’s space sector is at a pivotal moment of transformation, with private sector innovation fueling an era of unprecedented growth and possibilities. Historically led by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), the space domain is now witnessing the rise of agile, technology-driven startups and private companies that are reshaping the nation’s space ambitions. This report delves into the factors behind this dynamic shift—from policy reforms to technological advancements—and explores the vast potential of India’s space-tech industry. With a unique combination of cost-effective engineering, skilled talent, and progressive policy support, India is positioning itself as a global hub for commercial space activities and innovation. This exciting journey underscores the shift from state-led space missions to a private-sector-led industry that could see India lead in space tech and exploration on a global stage.

In recent years, the space sector in India has undergone a dramatic shift. What was once a domain exclusive to state-led missions and large government initiatives is now brimming with the entrepreneurial spirit of private players. A slew of startups, from satellite manufacturers to launch service providers and space-based data companies, are entering the industry, catalyzed by supportive policies and market demand. The ambition is clear: these private players aim to make space accessible, affordable, and technologically advanced, putting India on the global map as a competitive force in space-tech.
Innovative Indian startups like Skyroot Aerospace, Pixxel, and Agnikul Cosmos are capturing the world’s attention by focusing on low-cost, high-performance solutions. For instance, Pixxel's work in Earth-imaging satellites and Agnikul’s small satellite launch vehicles illustrate a future where India’s space companies will not only fulfil national needs but also compete globally, catering to international clients seeking economical space solutions. This entrepreneurial rise is carving out a new chapter in India’s storied space journey, where the private sector and ISRO are set to collaborate, amplifying each other’s strengths.
India’s space journey began with ISRO, established in 1969 under the visionary leadership of Dr. Vikram Sarabhai. Over the decades, ISRO built a reputation for innovation, resourcefulness, and achieving complex space missions at a fraction of the cost typically seen in global space programs. Milestone achievements like the Mars Orbiter Mission in 2013—accomplished on a budget lower than that of a Hollywood movie—cemented ISRO’s position as a trailblazer in cost-effective space exploration. Chandrayaan, India’s lunar exploration program, further elevated India’s standing as a capable space-faring nation, paving the way for ambitious missions in interplanetary exploration.
However, as global space activities expanded and private sector-led innovations in space became the norm, India began to recognize the benefits of involving private companies in its space ecosystem. A shift was needed to meet the growing demands of commercial space activities, satellite launches, and space-based data services. This shift is now taking place, as the Indian government invites private companies to join ISRO in building a robust, globally competitive space industry that can not only fulfill domestic needs but also serve international markets.
A major factor in the rise of private space-tech in India is the wave of policy reforms over the past few years. In 2020, the Indian government launched a comprehensive set of reforms to liberalize the space sector. One of the most transformative changes was the establishment of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe), which serves as a regulatory body and gateway for private companies seeking to enter the space industry. This unprecedented move provides a structured framework for private companies to partner with ISRO, access its infrastructure, and leverage its expertise while pursuing independent projects and innovations.
Moreover, the introduction of policies like SpaceCom, aimed at satellite communication, and SpaceRS, for remote sensing, has given private players the confidence to invest in India’s space ecosystem. These policies simplify licensing, ensure transparency, and encourage private companies to participate in activities like satellite building, data services, and launch operations. By fostering public-private partnerships and facilitating foreign investments, India’s new space policies are set to unlock opportunities that could transform it into a top-tier global space economy.
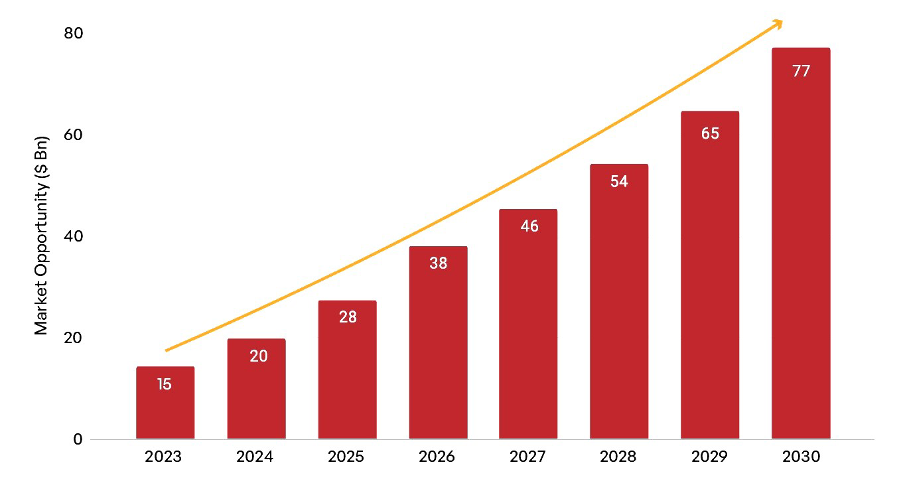
India’s space-tech industry, currently valued at approximately $10 billion, is expected to grow at a rapid pace, potentially reaching $50 billion by 2024. This growth is driven by rising demand for satellite-based services like telecommunications, Earth observation, and internet connectivity. For instance, as 5G rolls out across India and the need for remote connectivity solutions rises, satellite services will become increasingly valuable, opening doors for private firms to tap into this market.
Globally, the space industry is projected to become a trillion-dollar economy by 2040, and India’s cost-effective solutions position it uniquely to capture a significant share of this market. Indian space-tech startups are capitalizing on this opportunity by developing affordable, reusable launch vehicles and cutting-edge satellite technology. For instance, companies like Skyroot Aerospace are pioneering small satellite launch systems that can carry payloads into low Earth orbit at competitive costs, making space missions more accessible and practical for international clients.
As international investments pour in, India’s private space sector is poised to generate high-skill jobs, foster innovation, and bolster scientific advancements. With its focus on cost-efficiency and innovation, the Indian space-tech sector could become a global leader in space services, providing solutions not only for national interests but also for global commercial ventures. India’s burgeoning space-tech market has the potential to revolutionize sectors from agriculture and disaster management to environmental monitoring and defence.
India’s space-tech startup ecosystem is brimming with innovation, driven by bold visions and groundbreaking technologies. Several startups have emerged as trailblazers, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible and positioning India as a leader in cost-effective space solutions. Here are some of the most inspiring success stories:

Skyroot Aerospace made history as the first private Indian company to successfully launch a rocket, showcasing the capabilities of India’s nascent private launch sector. Their Vikram series of missiles is designed for cost-effective, on-demand launches, enabling domestic and international clients to deploy small satellites. Skyroot’s successful mission underscores India’s growing expertise in affordable launch solutions and proves the potential of homegrown rocket technology. With reusable technology in development, Skyroot Aerospace is set to make a significant mark on the global space launch market.
Remarkable Feats-
Pixxel is transforming the way we understand our planet by developing a constellation of hyperspectral imaging satellites. Unlike traditional imaging, Pixxel’s technology captures data across hundreds of wavelengths, allowing for precise Earth monitoring. This capability has applications in agriculture, environmental monitoring, and disaster management, enabling decision-makers to gain insights into crop health, pollution levels, and natural resource management. By democratizing access to high-quality, real-time Earth observation data, Pixxel is positioning itself as a leader in satellite-based analytics for critical sectors worldwide.
Remarkable Feats-

Agnikul Cosmos stands out for its groundbreaking work in 3D-printed rocket engines. Their Agnibaan rocket, tailored for launching small satellites, features a fully 3D-printed engine, reducing manufacturing time and costs. This technological edge enables Agnikul to quickly build rockets tailored to specific mission requirements, offering customized, low-cost launch services. Agnikul’s advancements in additive manufacturing for aerospace highlight India’s strength in high-tech, cost-efficient solutions, appealing to the growing demand for flexible launch capabilities in the small satellite market.
Bellatrix Aerospace is leading the way in propulsion technology, developing a suite of innovative, eco-friendly propulsion systems. Their patented electric and green chemical propulsion systems are engineered to extend satellite lifespans and improve maneuverability, essential for high-precision space missions. Bellatrix’s breakthrough technologies, such as their microwave electro-thermal thruster, offer fuel-efficient, cost-effective solutions for satellite and space exploration applications. These advancements not only enhance mission flexibility but also contribute to sustainable space operations.
Total Funding Raised (2014–2024): Indian space-tech startups have collectively attracted over $285 million in investment since 2014, a significant increase driven by government reforms and growing global interest
2020: Approximately $10 million across early-stage investments, primarily seed and Series A rounds.
2021: Funding increased to $45 million, with investments led by venture capital firms interested in satellite tech and analytics.
2022: Over $100 million in funding, marking a major milestone with substantial investments in companies developing launch vehicles and satellite-based solutions.
2023: Continued growth, with funding rounds reaching $80 million, bolstered by international investors and grants from the government.
2024: Expected to exceed $50 million, as startups secure additional rounds for scaling up manufacturing and infrastructure.
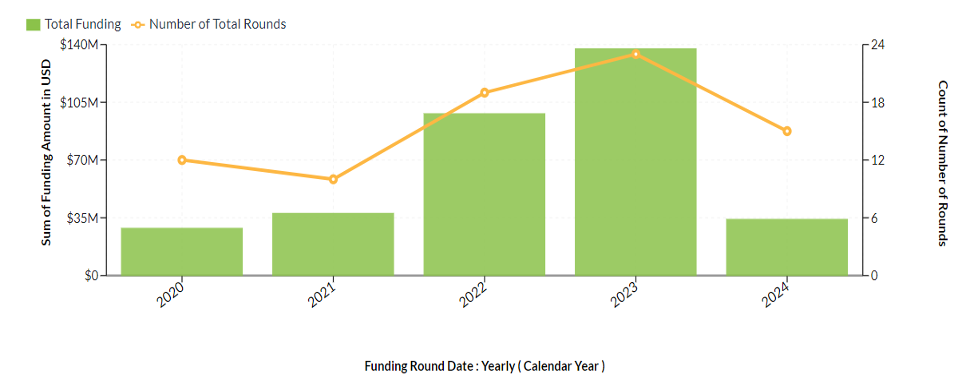
Average Funding per Startup (2024): Startups are raising between $5–$30 million per round, depending on the maturity stage and scope of the project.
Projected Future Funding (2025–2030): With industry-friendly policies and global demand for satellite data, cumulative investments are expected to exceed $1 billion by 2030, with an annual compound growth rate (CAGR) of 26%.
With demand for satellites on the rise, there’s a substantial market for satellite manufacturing and related services in India. From telecommunications and broadcasting to navigation and Earth observation, the need for satellites is expanding rapidly. Indian startups, with their focus on affordability and efficiency, are well-positioned to manufacture small satellites that cater to both domestic needs and international markets, making this a lucrative area for investment and growth.
Affordable and reliable launch vehicles are a critical need in today’s space economy, especially for small satellite launches. Indian companies like Skyroot and Agnikul are pioneering cost-effective launch solutions that can be tailored to specific mission needs, making them appealing options for international clients seeking economical launches. With global interest in frequent, low-cost satellite launches, India’s launch vehicle market is poised for exponential growth.
The demand for real-time, high-resolution Earth observation data is growing across sectors such as agriculture, disaster management, and climate monitoring. Companies like Pixxel are leveraging advanced imaging technology to provide insights that drive decision-making and optimize resource management. This sector offers significant potential for growth, with applications in both public and private sectors, ranging from precision farming to urban planning.
Data analytics for space applications is an emerging sector with high demand, especially as satellite data becomes more accessible. Indian startups are developing AI-driven platforms to process and interpret large volumes of space-based data, delivering actionable insights for industries like insurance, logistics, and environmental conservation. As data from space becomes increasingly important for day-to-day business decisions, space data analytics is a field ripe for innovation.
Ground stations play a vital role in satellite communication, telemetry, and data reception. As the number of satellite launches increases, there is a growing need for ground station networks to support these missions. India’s cost-effective engineering capabilities and strategic geographic position make it an ideal hub for ground station services, which can cater to both domestic and international clients.
India’s space sector is experiencing a “golden hour,” where supportive policies, global market demand, and technological advancements converge to create the perfect environment for growth.
The establishment of IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center) has been a game-changer for private players in India’s space industry. IN-SPACe serves as a bridge between the government and private companies, simplifying the approval process, facilitating partnerships with ISRO, and providing a clear regulatory framework. This support not only reduces entry barriers but also creates a collaborative environment that encourages innovation, making it easier for startups to navigate and contribute to the space sector.
As more industries recognize the value of satellite data and services, global demand for space-based solutions is on the rise. The increase in satellite-based applications across sectors—such as telecommunications, environmental monitoring, and defense—presents an enormous market for Indian companies. With India’s reputation for cost-effective, high-quality engineering, local space-tech firms are positioned to capture this growing demand and establish a robust client base in international markets.
Advancements in manufacturing, materials science, and 3D printing are driving down the costs of space technology. For instance, Agnikul’s use of 3D-printed engines demonstrates how technology can reduce production costs while increasing design flexibility. These technological breakthroughs make it more feasible for startups to enter the space sector, reducing capital requirements and enabling a more diverse set of players to contribute to space innovation.
India boasts a highly skilled talent pool, with engineers and scientists trained at premier institutions such as the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and the Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST). ISRO’s decades of experience in pioneering space missions have also created a seasoned workforce with deep expertise in space technology. This rich talent base provides Indian space-tech startups with a strong foundation of knowledge and skills, enabling them to compete on a global scale and innovate at a rapid pace.
Starting a venture in the space-tech industry requires a blend of technical expertise, strategic planning, and access to resources. As India’s space-tech ecosystem grows, aspiring entrepreneurs and professionals have more options to build a foundation in this exciting field.

The space-tech sector requires expertise in various technical fields. Each domain plays a critical role in the success of a space mission or technology. Key domains include:
A successful career in space tech demands a combination of technical skills, regulatory knowledge, and innovation. Key skills include:
Incubation programs provide crucial support to space-tech startups, offering access to funding, mentorship, and technical resources. Key programs include:
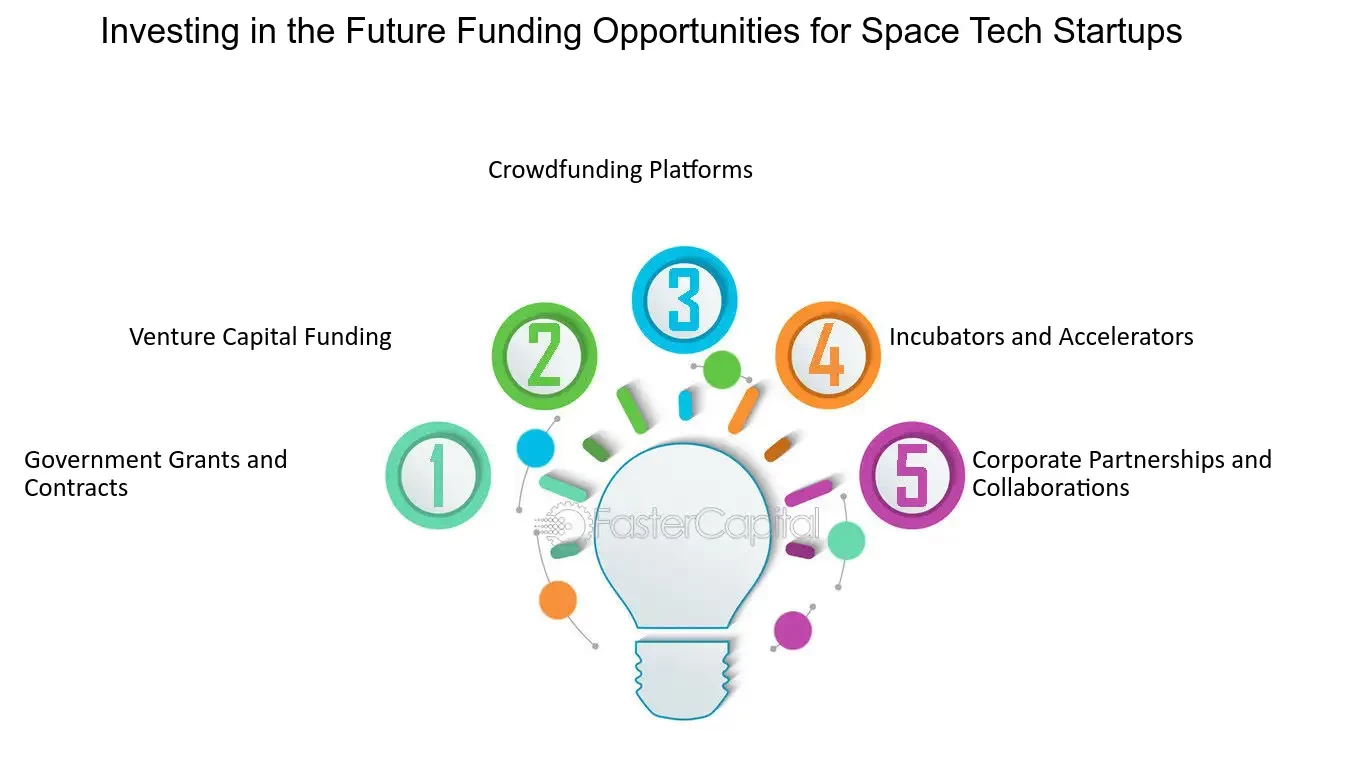
Securing funding is essential for space-tech startups due to the capital-intensive nature of the industry. Funding sources include:
Space-tech startups face unique challenges due to high costs, stringent regulations, and technical complexity. Here are some common challenges and solutions:
Space tech has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries, driving sustainable development and innovation.
Satellite data and space-based IoT systems can play a pivotal role in building smart cities, helping manage resources, monitoring infrastructure, and enhancing public services. For example, satellite-based mapping aids in urban planning, while real-time data from space can optimize traffic flow and energy usage in cities.
Space-tech applications in agriculture are transforming how crops are managed and monitored. Earth observation satellites can assess soil health, monitor crop growth, and provide early warning of pests or drought. By enabling data-driven decision-making, precision agriculture enhances productivity and supports sustainable farming practices.
As costs decrease and technology advances, space tourism is becoming a real possibility. Companies worldwide are developing passenger flights to low Earth orbit, and Indian startups have the opportunity to support or partner in this emerging sector. The development of reusable rockets and cost-efficient launch systems in India can help make space tourism more accessible.
Satellites provide critical data for tracking climate change, deforestation, ocean health, and pollution. With Earth observation technology, India’s space-tech sector can contribute valuable insights for climate action and conservation efforts, helping governments and organizations make data-driven decisions on environmental policies.
In healthcare, space tech can improve connectivity in remote areas and facilitate telemedicine, emergency services, and mobile health applications. Satellite communications enable healthcare access in regions without ground infrastructure, helping to bridge healthcare gaps across India.
Satellite-based internet can bring high-speed connectivity to underserved rural areas, opening up new possibilities for digital education, remote learning, and online services. Space-tech can help India achieve digital inclusion, empowering students and professionals in remote locations with access to global resources.
Satellite data is integral for tracking and managing supply chains and logistics operations. From route optimization for shipping to real-time monitoring of goods, space tech enhances efficiency and reduces costs in logistics. It also supports the development of autonomous vehicles and UAVs by providing accurate mapping and navigation data.
India’s space-tech industry is set for a promising future, marked by advancements in technology, growing demand, and international collaboration.
Key trends include the miniaturization of satellites, advances in reusable rocket technology, and AI-driven space data analytics. Additionally, the shift toward small, cost-effective satellite constellations is opening new avenues for startups, especially in Earth observation, IoT, and broadband connectivity. Innovations in 3D printing and additive manufacturing are further reducing costs and expanding capabilities for space-tech startups.
The global space economy is projected to reach $1 trillion by 2040, with India’s share growing steadily as it expands into commercial markets. Indian space-tech startups are expected to capture a larger portion of the global satellite services and launch market, thanks to their affordability and innovation. With increasing demand for remote sensing, satellite internet, and space-based analytics, the Indian space-tech market is poised for significant growth.
Collaborations with international space agencies and private entities present enormous opportunities for Indian space-tech. Partnerships with NASA, ESA, and private space companies can lead to joint missions, technology exchange, and new market opportunities. These collaborations also help startups meet international standards and expand their client base globally, positioning India as a major player in the global space economy.
India’s space-tech industry is on a remarkable trajectory, fueled by innovation, talent, and a supportive ecosystem. With continued focus on policy, technology, and international cooperation, India is well on its way to becoming a leader in space technology, contributing solutions that impact not only its economy but the entire world. The future of Indian space tech holds immense promise, with boundless possibilities for exploration, collaboration, and growth.